What Are AI Agents? A Deep Dive Into the Essentials with Hw Infotech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized technology by creating systems capable of performing tasks that traditionally required human intelligence. At the heart of many AI applications lie AI agents, which interact with environments, perceive data, and take actions to achieve specific goals. Understanding intelligent agent in AI, knowledge-based agents in AI, and types of agents in AI is crucial for developers, researchers, and businesses aiming to leverage AI for strategic advantage.
This article provides a comprehensive guide on the structure of agent in AI, model-based agent in AI, and other key concepts to deepen your understanding of AI agents.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is an autonomous entity that perceives its environment through sensors, processes information, and takes actions using actuators to achieve specific objectives. AI agents are fundamental in AI because they provide a structured approach to problem-solving, decision-making, and automation.
Formally, an AI agent is defined as:
Agent=Architecture + Program\text{Agent} = \text{Architecture + Program}Agent=Architecture + Program
- Architecture: The underlying hardware or software that hosts the agent.
- Program: The algorithm or logic that defines the agent’s behavior.
AI agents operate in diverse fields such as autonomous vehicles, recommendation systems, robotics, and virtual assistants.
According to Statista (2024), the global AI software market is expected to reach $126 billion by 2025, with intelligent agents playing a key role in driving automation and analytics solutions.
Structure of Agent in AI
The structure of agent in AI typically consists of three key components:
- Sensors: Devices or functions that collect data from the environment.
- Example: Cameras, microphones, temperature sensors, or software APIs.
- Effectors/Actuators: Components that enable the agent to act on its environment.
- Example: Robot arms, motors, display screens, or network commands.
- Agent Program: The decision-making logic that determines the action based on percepts from sensors.
This architecture allows AI agents to process inputs, maintain internal states, and perform goal-directed actions.
Intelligent Agent in AI
An intelligent agent in AI refers to an agent capable of autonomous decision-making, learning from experiences, and adapting to new situations. Intelligent agents are defined by the following characteristics:
- Autonomy: Ability to operate without human intervention.
- Reactivity: Respond to environmental changes in real-time.
- Proactiveness: Take initiative to achieve goals rather than merely reacting.
- Social Ability: Communicate or collaborate with other agents or humans.
Example Applications of Intelligent Agents:
- Autonomous cars analyzing traffic data to navigate safely.
- Virtual assistants like chatbots providing personalized responses.
- Industrial robots adapting assembly-line tasks based on sensor input.
Research by McKinsey (2023) shows that AI-driven autonomous agents could increase productivity in enterprises by up to 40% over the next decade.
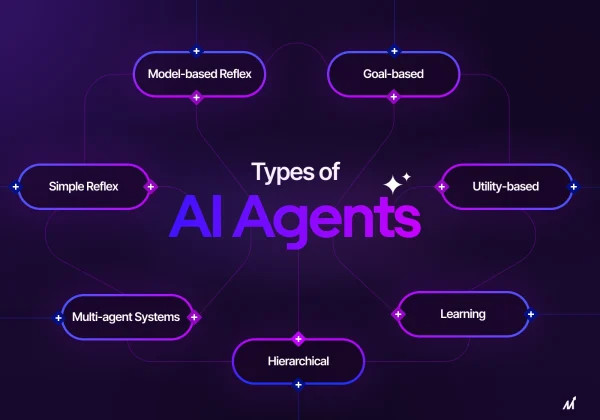
Types of Agents in AI
Understanding the types of agents in AI is essential for selecting the right approach for specific tasks. The main categories include:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
- Operate on condition-action rules (if-then).
- Do not maintain internal state.
- Suitable for predictable environments.
Example: A thermostat adjusting temperature based on current readings.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
- Maintain an internal model of the environment.
- Decisions depend not only on current percepts but also on past states.
Example: Autonomous vehicles tracking past positions of surrounding cars.
3. Goal-Based Agents
- Take actions to achieve specific goals.
- Evaluate possible future states and select actions that maximize goal achievement.
Example: A chess-playing AI planning several moves ahead to checkmate an opponent.
4. Utility-Based Agents
- Consider multiple goals and choose actions that maximize a defined utility function.
- Useful in complex decision-making with trade-offs.
Example: Ride-hailing apps assigning drivers to passengers based on distance, traffic, and earnings.
5. Learning Agents
- Improve performance over time using past experiences.
- Can adapt to dynamic and uncertain environments.
Example: Recommendation systems like Netflix or Amazon, which refine suggestions based on user behavior.
Knowledge-Based Agents in AI
Knowledge-based agents in AI are advanced agents that store knowledge about the environment and use reasoning to make decisions. Unlike simple reflex agents, they can deduce new information and solve complex problems.
Key Features:
- Knowledge Base: Stores facts and rules about the environment.
- Inference Engine: Uses logical reasoning to derive new knowledge or make decisions.
- Perception System: Updates the knowledge base with new information from the environment.
Applications:
- Expert systems for medical diagnosis.
- Fraud detection in banking.
- Predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
Knowledge-based agents are critical in domains where decision-making involves complex reasoning and planning.
Model-Based Agent in AI
A model-based agent in AI maintains an internal representation of the world to track the consequences of actions.
Components of a Model-Based Agent:
- Internal Model: Represents how the environment works, including causal relationships.
- State Tracker: Keeps track of current and past percepts.
- Decision Module: Uses the model to select the best action for achieving goals.
Advantages:
- Better performance in partially observable environments.
- Can handle dynamic and uncertain scenarios effectively.
Example: A drone navigating through changing weather conditions by updating its model of wind speed and obstacles.
Facts and Figures About AI Agents
- Gartner predicts that by 2025, 70% of enterprises will deploy AI agents for operational tasks, up from 30% in 2022.
- AI agents are estimated to handle 40% of routine customer service queries in large organizations by 2026 (Forrester Research).
- Model-based and knowledge-based agents reduce error rates in automated processes by up to 35% compared to traditional rule-based automation.
- Intelligent agents can improve decision-making speed by 50-60% in dynamic environments.
These statistics highlight the growing adoption and impact of AI agents across industries.
Challenges in Implementing AI Agents
Despite their advantages, AI agents face several challenges:
- Complexity: Building model-based and knowledge-based agents requires expertise in AI, machine learning, and domain knowledge.
- Data Dependency: Accurate AI agents need large amounts of high-quality data.
- Interpretability: Some agents, especially learning agents, act as “black boxes,” making it difficult to explain decisions.
- Ethical Concerns: Autonomous agents raise ethical issues regarding accountability and decision-making.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Deploying AI agents requires seamless integration with current IT infrastructure.
Addressing these challenges involves robust planning, iterative testing, and ongoing monitoring.
Applications of AI Agents
1. Autonomous Vehicles
AI agents process real-time sensor data to make driving decisions. They predict traffic patterns, detect obstacles, and plan optimal routes.
2. Healthcare
Knowledge-based agents support medical diagnosis, personalized treatment recommendations, and predictive analytics for patient care.
3. Finance
AI agents monitor transactions, detect fraud, and optimize investment strategies using predictive modeling.
4. Smart Homes
Intelligent agents control lighting, HVAC, and security systems based on environmental data and user preferences.
5. E-Commerce
AI agents provide personalized recommendations, dynamic pricing, and automated customer support to enhance the shopping experience.
Future Trends in AI Agents
- Multi-Agent Systems (MAS): Collaborative AI agents working together to solve complex problems.
- Cognitive Agents: Agents capable of reasoning, learning, and understanding human-like knowledge structures.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Making AI agent decisions transparent and interpretable.
- Integration with IoT: AI agents controlling and optimizing interconnected devices in real-time.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: Expanding AI agents in areas like logistics, supply chain, and smart cities.
These trends indicate that AI agents will become increasingly sophisticated, autonomous, and integral to business and daily life.
Conclusion
AI agents, including intelligent agents in AI, knowledge-based agents in AI, and model-based agents in AI, are at the core of modern automation and decision-making. Understanding the types of agents in AI and the structure of agent in AI allows businesses and developers to design systems that are efficient, adaptive, and capable of operating in dynamic environments.
With increasing adoption across industries—from autonomous vehicles to healthcare and e-commerce—AI agents are set to transform how businesses operate. For enterprises seeking expert guidance in implementing AI agents for operational efficiency and innovation, Hw Infotech provides comprehensive solutions to help organizations leverage AI effectively.
